Home - Technology - PEMFC
PEMFC
Proton-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
A Promising Technology for Sustainable Energy
Proton-exchange membrane fuel cells are a type of fuel cell that has gained significant attention in recent years due to their potential for a wide range of applications. They typically convert hydrogen into electrical energy through an electrochemical process.
PEMFC Components
-
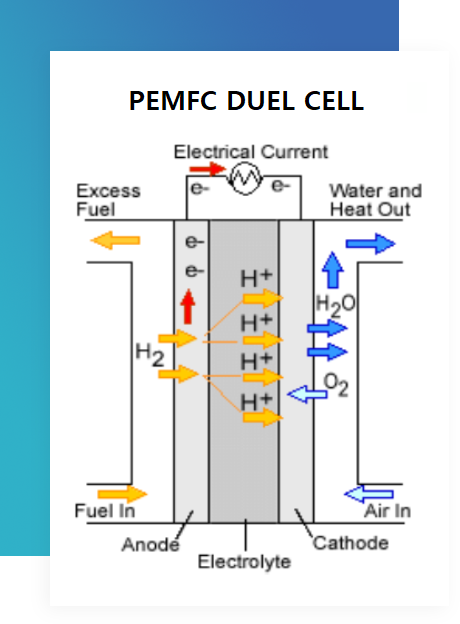
Anode
The anode is where the fuel (hydrogen) is oxidized, releasing electrons and protons.
-
Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM)
The PEM acts as a barrier that allows protons to pass through while blocking electrons.
-
Cathode
The cathode is where oxygen reduction occurs, combining electrons from the anode with oxygen molecules to form water.
Advantages of PEMFCs
-
Low Operating Temperature
The anode is where the fuel (hydrogen) is oxidized, releasing electrons and protons.
-
High Power Density
PEMFCs can achieve high power densities, enabling them to power compact and lightweight devices.
-
Quick Start-up and Shutdown
PEMFCs can start up and shut down quickly, making them well-suited for transportation applications.
-
Low Emissions
PEMFCs produce only water and heat as byproducts, contributing to minimal environmental impact.
Applications of PEMFCs
-
Transportation
PEMFCs are being developed for use in electric vehicles, buses, and even ships.
-
Stationary Power
PEMFCs can be used as stationary power sources for backup power, remote communities, and off-grid applications.